Search Our Whole site:
Just Search: Bangladesh
Mobile-powered employment opportunities for all; i2i challenge call for Bangladesh
People with disabilities are creative leaders within workforces however are often unable to access employment opportunities or progress within careers. Mobile technology can act as a bridge to employment opportunities by helping people learn skills, increasing awareness of job opportunities and helping to get and retain employment opportunities. The i2i programme, funded by UK Aid and led by Leonard Cheshire has teamed up with Global Disability Innovation Hub (GDI Hub) and SBK Foundation to launch the mobile innovation challenge for employment for all. Up to £20,000 is available to support winning applicants in the development of employment solutions focused around mobile in Bangladesh with access to global expertise from GDI Hub and local innovation networks and support through SBK Foundation. Applications close on 14th March 2021, with projects completed by November 2021.
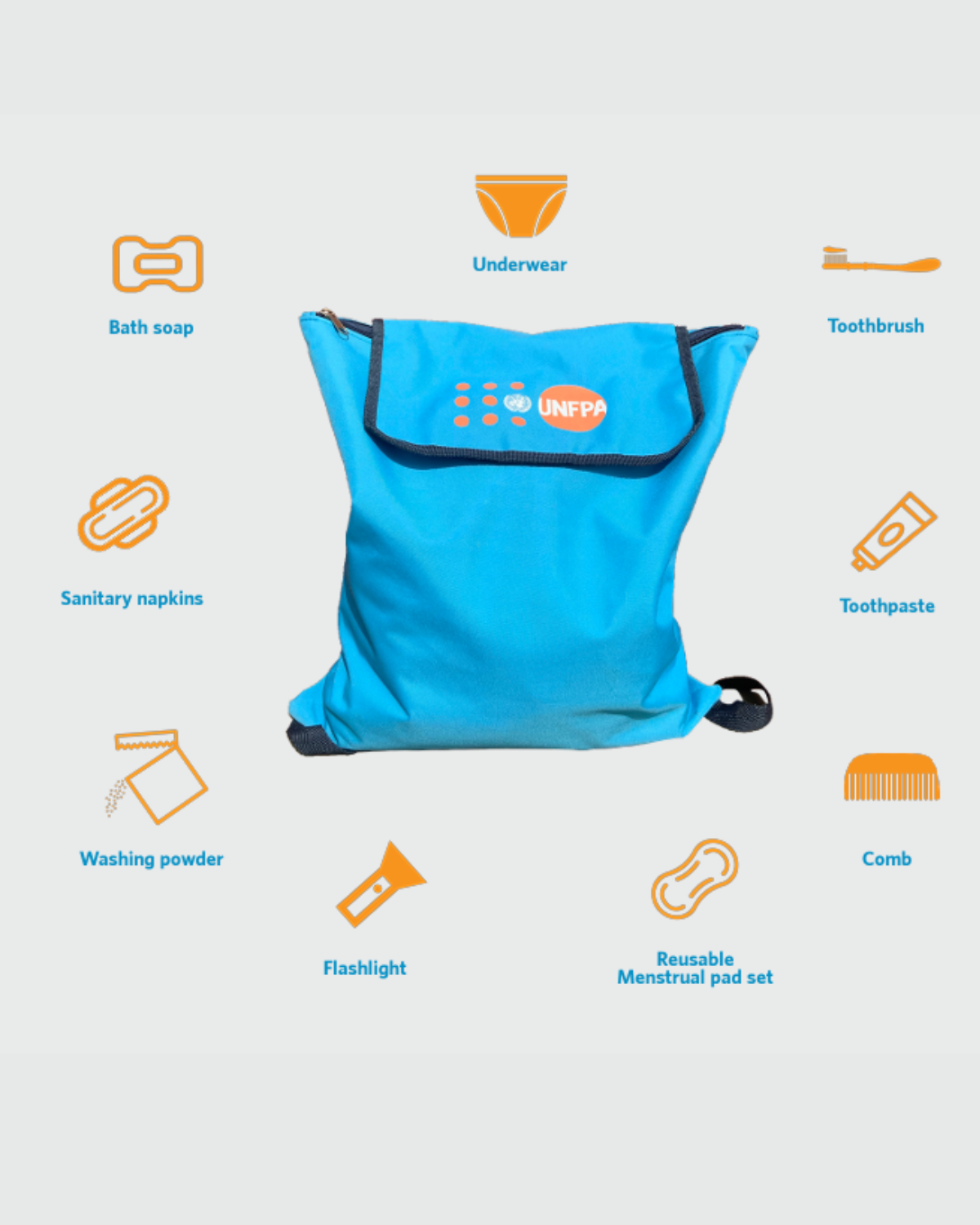

Customising Dignity Kits and Menstrual Health Management Kits with women and girls with disabilities in Bangladesh with UNFPA
As part of the AT2030 gender workstream, we have collaborated with UNFPA, the United Nations Population Fund Asia-Pacific Regional Office (APRO), on a match-funded project which aims to capture the lived experiences of women and girls with disabilities and identify their specific needs during crises and humanitarian situations. In March 2024, we held consultation workshops with the UNFPA-Bangladesh Country Office to consult with partners and stakeholders to discuss how the content of existing Dignity Kits (DKs) and Menstrual Health Management Kits (MHM Kits), often distributed during humanitarian crises, meet the needs of women and girls with disabilities

Exploring the experience of persons with disabilities of using mobile technology in their daily lives in Kenya and Bangladesh
Although, mobile phones are universally used for communication, for persons with disabilities they become essential assistive technologies that bridge barriers to opportunities which are not accessible otherwise.

Assistive Technology in Two Humanitarian Contexts: Bangladesh and Jordan
Despite increased focus on the need for assistive technology (AT), very little is actually known about how people who need AT are managing in humanitarian contexts. This research found that the provision of AT (in this case mainly assistive devices) is ad hoc, and largely related to the access, availability and focus of NGO-funded projects in camps or communities.
Mobile-powered employment opportunities for all; up to £20k available for Bangladesh solutions
The UK aid funded i2i programme has launched a mobile innovation challenge for employment for all, using mobile technology to bridge to employment opportunities by the development of skills, increasing awareness of job opportunities and helping disabled people to get and retain employment opportunities. Up to £20,000 is available to support winning applicants in the development of employment solutions focused around mobile in Bangladesh.

Video: How does mobile empower me? Sumona’s story
Sumona Khan lives in Dhaka, Bangladesh. She is preparing herself for a government job. Sumona earns income through mobile. She records books for blind users.

Understanding the mobile disability gap
There has been limited research to understand access to mobile phones by persons with disabilities and the impact of mobile technology in their lives. This research aims to bridge the knowledge gap and to understand the potential of mobile phones as assistive technologies (ATs) for persons with disabilities in Kenya and Bangladesh. It presents an evaluation of the gap and barriers to mobile phone ownership experienced by persons with disabilities, as well as the usage patterns of four main mobile-enabled services (voice, SMS, mobile internet and mobile money) and the role of mobile phones to enable access to basic services, such as education, healthcare, transportation, employment and financial services.

Inclusion and Independence: The impact of Mobile Technology on the Lives of Persons with Disabilities in Kenya and Bangladesh
This paper presents the findings of a participatory photovoice study looking at the role that mobile phones play in the daily lives of 16 persons with disabilities in Kenya and Bangladesh.
Techshare Pro 2019: The Future of Accessibility and Inclusive Design
A recording from Techshare Pro 2019 where GSMA presented their findings on the mobile disability gap in Bangladesh and Kenya.

Assistive Technology in Two Humanitarian Contexts, Bangladesh and Jordan
Despite increased focus on the need for assistive technology (AT), very little is actually known about how people who need AT are managing in humanitarian contexts. This research found that the provision of AT (in this case mainly assistive devices) is ad hoc, and largely related to the access, availability and focus of NGO-funded projects in camps or communities. Devices alone cannot ensure wider inclusion – for that, there still needs to be attitudinal change, environmental adaptations, better provision of resources (including rehabilitation) and much wider awareness about the policies and legislation that support the rights of persons with disabilities, including those who have crossed an international border to seek safety and security.